When it comes to industrial cutting methods, you have many different options to choose from. Two of the most common are plasma cutting and laser cutting. Although they sound alike, they’re often used for different things. So, what is the difference between plasma and laser cutting?
| Plasma Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|
| Uses gas to create plasma which cuts material | Uses a high-power CO2 laser to cut material |
| Can cut through metal >25mm thickness, cheaper to operate | Fast cutting speed, higher precision, can cut more than metal |
| Produces harmful gas and radiation, cuts are not as clean | Cannot cut through very thick metal, expensive to operate |
While that’s a basic breakdown, it is more complicated than that. We’ll go into their history, best applications, the benefits and drawbacks of each, and much more in detail below.
Table of Contents
Laser Cutting Versus Plasma Cutting
In order to have mass production of metal goods, you need to be able to cheaply and quickly cut custom pieces from larger metal sheets. Over the years people have come up with many different ways to make this happen, including:
- Using cutting wheels (“turning metal”)
- Using high pressure water jets
- Flame cutting
- Plasma cutting
- Laser cutting
While all of these are methods to achieve the same goal, they still have many differences between them. Plasma and laser cutting are two of the most popular methods used today, so let’s explore the differences between them in detail.
Origins and Explanation of Both Methods
In order to understand the modern differences between plasma and laser cutting, it can be helpful to understand when they were developed and for what reason. We’ll also talk a little about how they work—a must-know if you’re going to be dealing with them.
Plasma Cutting: What Is It and How Does It Work?
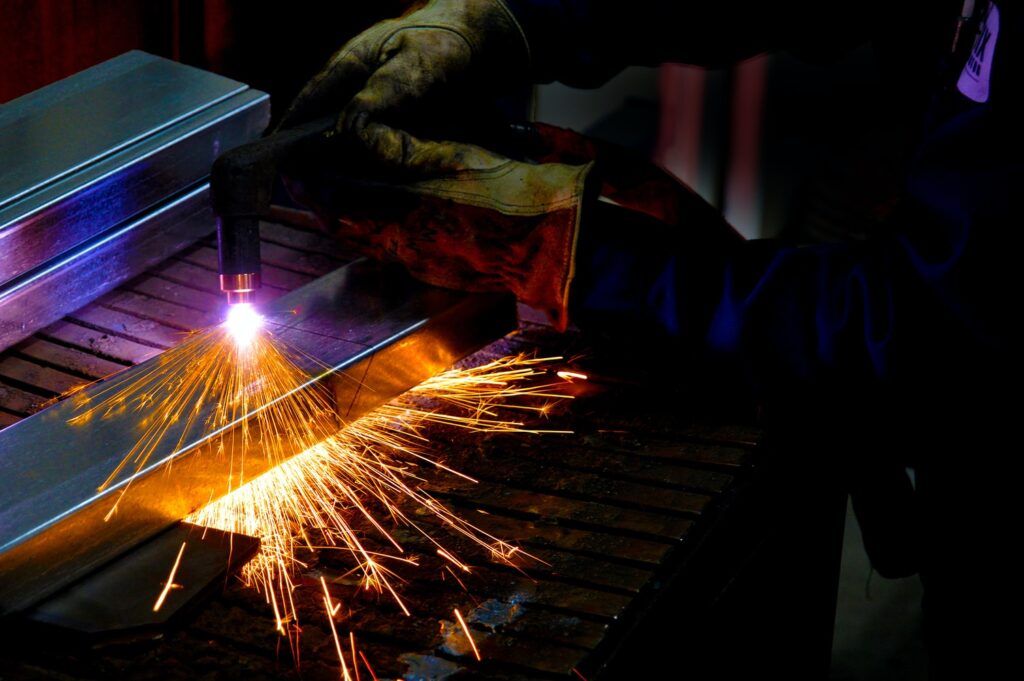

The method of producing and using plasma to cut through metal was first patented in the 1950s. Back then, if you wanted a specific piece cut from a metal sheet then your main option was to have it cut out with a regular oxyacetylene torch. However, plasma cutting didn’t catch on until the 1970s because that’s when:
- A lot of industrial factories were using gantry machines, which is the crane that holds the torch above the cutting piece and moves it around
- The methods used in plasma cutting were more developed
- The cost of using plasma to cut also dropped
With all of those things in place, it set the stage for plasma cutting to jump in and become one of the most popular and effective methods.
Plasma cutting works like this:
- Gas (usually nitrogen) flows down the tube and out the cutting head
- An electrode inside the tube of the cutting head creates a highly charged electrical arc between itself and the metal to be cut
- This arc is extremely hot, and as it arcs through the flowing gas inside the cutting head it superheats it into the fourth state of matter, plasma
- The plasma is squeezed through a very tight opening in the cutting head as it exits, which increases its speed significantly
- The incredibly hot plasma moving at a very high-speed cuts through the metal below it
That’s the basic explanation. In reality, there is a lot of physics and chemistry going on in to make it happen, and plasma cutting heads are precisely engineered.
Laser Cutting: What Is It and How Does It Work?
Using a laser to carve up material sounds like something out of a sci-fi novel. However, this technology dates back to the 1960s when the Western Electric Engineering Research Center produced a machine capable of drilling holes with a laser. From there, the tech received a lot of development over the years, including:
- Further precision modifications for aerospace engineering tasks
- Adapting different types of lasers to cut different materials
- Optimizing the power usage to make it more efficient
In modern manufacturing, laser cutting continues to make strides and is quickly catching up to the abilities of other cutting methods.
Here’s how a laser cutting machine works:
- First, light is generated by “stimulating” a material with electric discharge or other method
- The extra energy added to the material causes it to emit photons or light
- The light emitted is filtered through internal mirrors until only the correct wavelengths for the application are left
- The laser is reflected down a tube and towards the cutting head
- The lens inside the cutting head focuses the laser on a single specified point and distance, greatly increasing its power and ability to cut
Laser cutting uses a lot of different methods for getting through material. Some of these methods include
- Vaporizing
- Cracking it with thermal stress
- Melting it and blowing it out of the way with high pressure gas
Benefits of Plasma Cutting
Plasma cutting remains one of the most popular cutting methods for certain applications, and it has many qualities that make it an excellent choice. We’ll explain more in detail below
Lower Startup and Maintenance Costs
Since plasma cutting has a long history of development and use, it means that it is almost always cheaper to use.
The initial equipment for cutting metals with plasma has a lower cost than a laser cutting setup. This allows you to spend more of your budget on upgraded models with:
- More cutting power
- A higher number of useful digital features
- Lots of backup nozzles and electrodes
That last point is essential. When using a plasma cutting machine, be prepared to spend extra money on the nozzles and heads as they will wear out. This does add a recurring cost to using a plasma cutter.

Can Cut Thick Materials
Plasma jets are extremely hot and moving extremely fast. While this does add some danger, it also means that it can punch through a lot more material. With advancements made in directing the plasma correctly, plasma cutting machines can cut through steel greater than 25mm in thickness.
Can Be Made Portable
Plasma cutting machines are typically more portable than laser cutting machines because they use gas instead of light. Since light has to be reflected in straight lines down to the cutting head, laser cutters require rigid structures, which leads to less portability.
Since plasma cutters just use gas and electricity as their source, you can have flexible hoses and overall a much more portable design. The nozzle itself could even fit inside a handheld cutting torch.
Drawbacks of Plasma Cutting
While plasma cutting is great for cheaply cutting thick material, it does also have its downsides. Chief among these are:
- The time it takes to cut thin materials
- The dangerous byproducts of plasma cutting
- The extra time needed to refine the cut products
Cutting Materials Can Take More Time
For various reasons, plasma cutting heads cannot cut certain depths and materials as quickly as a laser cutter. Especially when cutting thin sheets of materials, the plasma cutter falls behind a typical laser cutter.
However, this is not always the case. Surprisingly, when it comes to cutting medium-thickness sheets, a plasma cutter can often outpace a laser cutter because of the way it cuts. Still, for thin sheets, it is much slower.
Plasma Cutting Produces Dangers
Forcing a jet of superheated plasma through a sheet of metal is just about as dangerous as it sounds. Thankfully there are many safety features and regulations in place. Still, this doesn’t mean all the dangers are eliminated, and there are some things you should be aware of:
- Radiation created from the plasma can damage the cells in your eyes and burn your skin, much like welding
- Depending on the type of material and gas being used, harmful gases can be produced by the cutting process which requires special precaution
- Hot slag created from the cutting process can sometimes act unexpectedly.
Various numbers of shields, guards, software and hardware level safety features, and good shop safety can drastically reduce these dangers.
It Can Leave Rough Product
While plasma cutting is still a precisely engineered process, there are just things that are hard to overcome because of the method used to cut. One of these is excess slag or molten metal produced by the process.
It very rarely poses a safety concern, but it still impacts the production process. The cuts with a plasma cutter almost always need cleaning up afterward. These include
- Smoothing
- Polishing
- Grinding away and solidified slag

Benefits of Laser Cutting
Vaporizing material with a laser not only sounds cool, it brings a lot of great benefits to the manufacturing process. We’ll cover a few of the more major ones in detail below.
Laser Cutting is Ultra Precise
Lasers can be focused to ultra-fine points, meaning that the cutting precision you can achieve with a laser far outstrips a plasma cutter. This allows more pieces to be cut from a single sheet as well as finer details to be added.
Lasers Can Cut Very Fast
The cutting speed of a laser cutter is a bit complicated. It depends on a lot of factors, such as:
- Material
- Cutting depth
- Angle
- The reflectivity of the material
However, in general, when the laser cutting is working on thinner sheets of material, it can cut much faster than a plasma cutter. The story changes as the material gets very thick, but a laser can burn through thinner plates of metal faster than any other cutting method.
Lasers Can Cut More Than Metal
One of the biggest advantages of a laser cutting device is its ability to cut much more than just metal. Laser cutters can cut all sorts of different materials, such as:
- Ceramics
- Textiles
- Plastics
- Rubbers
- Wood
The list of all the materials a laser can cut is too long to put here. Plasma may be good at cutting strong metals, but it’s just too rough and ineffective on other materials.
Lasers Produce Clean Cuts
Another factor in the overall precision of a laser cutter is the clean cuts it produces. Since the laser vaporizes its way through the material, there is little to no slag left behind.
The cut edges left behind after a laser cutter often need little to no cleanup, reducing the overall cost and effort of cutting pieces.
Drawbacks of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting devices work wonders in a lot of ways, but they are equally ineffective in some others.
Laser Cutters Cost More
Laser cutting technology isn’t necessarily that much newer than plasma cutting, but it is definitely newer in terms of broad industrial use. Because of this, both buying and maintaining laser cutting machines is more costly than the typical plasma cutter.
This is especially true if the buyer wants to stay on the cutting edge of the new laser cutting technology. There are many different ways and types of producing and directing a laser to cut, including:
- CO2 stimulation via electric pulse
- CO2 stimulation via RF radiation
- Neodynium lasers (for boring holes)
- Neodynium-yttrium-aluminum-garnet (for very high-power applications)
High power, fiber directed lasers are going to cost a pretty penny—much higher than a similar plasma cutting machine.
Lasers Don’t Do Great with Thick Metal
While plasma jets can punch right through very thick sheets of metal, lasers can have a comparatively hard time keeping up. The thicker the material is, the longer and longer it will take to cut with a laser cutter. This relationship isn’t linear, either—due to some of the mechanics involved in laser cutting, the length of time required to cut thicker materials is not a linear equation.
Additionally, once most metals are thicker than 25mm then lasers probably won’t be able to effectively cut it at all. More and more developments occur every year to help expand their cutting ability, but currently they cannot cut as thick of metal as plasma cutters can.

How to Choose Which Method to Use
Now that you know a little bit about the history, benefits, and drawbacks of each type, we’ve put together a few considerations to keep in mind when choosing which method to use for your project.
These tips can apply to whether you are only having a few pieces cut by another shop or if you are looking to invest in either type of machine yourself.
How Intricate Is Your Piece?
The first question to ask is how intricate and detailed your pieces need to be. As we discussed above, if your pieces require fine detail then a laser cutting solution is the best fit.
However, if your pieces don’t require an extreme degree of precision, then a plasma cutting method can be just as good. Plasma cutting machines are by no means imprecise—they are just less precise than the extreme precision of a laser cutter.
What’s Your Budget?
Budget can play a major or minor role in your decision depending on whether you are having pieces cut or directly buying the machine as a company.
If you are just looking to have some designs cut by a third party, then it just comes down to your needs rather than your budget. If your pieces require high precision, then have them laser cut. If not, then plasma cutting them will do just fine.
If you are looking to make an investment in an entire machine, then ask question like:
- Do I have a need for high-precision cuts at all?
- How often do I need to perform ultra-precise cuts?
- How much maintenance and replacing of heads do I want to do?
- Do I have the manpower or time to clean up cut surfaces?
- Will the ability to cut other materials than metal speed up my shop process?
At the end of the day, it comes down to the needs of your exact shop. If you never do precise cuts, and you don’t mind replacing cutting heads and cleaning up the cut edges, then a plasma cutting device may be a fine solution. If you plan to make enough precision cuts that it makes sense to do them in house rather than contract elsewhere, then a laser cutter could be a good investment.
Reduce Your Costs Through Good Design
How you design your pieces to be cut can have a large impact on your needs for the project. Smart design can often get around the unfortunate limitations of whatever machine you have on hand.
Here are some examples:
- Implementing more thin support structures instead of fewer thick supports can remove the necessity to cut pieces from thick materials
- Increasing the size of intricate pieces by a small margin may put them within a precision range your plasma cutter couldn’t previously match
The Difference Between Plasma and Laser Cutting
Plasma and laser cutting machines are both incredibly useful, high precision manufacturing devices. While they accomplish the same goal, they use different methods to do it. Remember that plasma cutting:
- Works by using a jet of superheated plasma to melt metal
- Is cheaper to operate and can cut very thick material
- Also is not as precise as laser cutting, and has some dangers
Laser cutters, on the other hand:
- Work by focusing a high-power laser to vaporize or melt material
- Are very precise and fast when cutting thinner materials
- Are also more expensive and cannot cut very thick metal
Now that you know the difference, their benefits and drawbacks, and some strategies to decide which to use, you have the tools to make an informed decision!





0 Comments